Vue- KDL¶
Why use Vue.js and Installation¶
Vue.js is a progressive framework built in Javascript that can build single paged application. It is also versatile and can be integrated into existing web pages. One of the biggest advantages of Vue is the ability to integrate and embed it into existing web projects. It is used only for front end development and is easy to learn using existing syntax pre-ES2015/ES6 standards. Vue.js is a great framework for people wanting to learn front-end development and for advanced users. [WhatIsVue]
The person behind the initial development behind Vue.js was Evan You. Evan originally worked at Google building web applications. He especially worked with the Angular front-end framework. He liked the framework so much, but he always felt like it was too resource heavy. Evan wanted to keep building web apps while using similar syntax as Angular. He then started the development of Vue.js. He decided to publish his work and made it to the front page of Hacker News. Vue.js became popular due to its ease of use. It’s a framework that is easy to learn but has enough to challenge to master. [HistoryOfVue]
Vue is similar to other frameworks, such as React in terms of the utilization of a virtual DOM and reactive components. Vue does perform better when it comes to rendering. It will render sub-components automatically since components are automatically tracked. In React, developers have to add additional keywords to avoid renders of the whole DOM. Vue achieves will only render the necessary components when changed.
Recently, Vue.js became the most popular front-end framework on Github in the terms of stars. One of the reasons Vue.js has picked up in speed in the last few years is due to its easy learning curve. It offers the ease of vanilla javascript syntax that most front-end developers are acclimated to. Other modern frameworks such as React and Angular require the knowledge of ES6 javascript, which has not yet been widely adopted.
Vue.js is also grabbing developer’s attention through its flexibility of being adapted into current web applications. Vue.js has the range to be used to build new applications or add onto existing web pages. Since its so flexible, developers can feel comfortable to use it at any level.
Vue.js is also light-weight framework compared to its counter-parts. A majority of users will leave a website if it takes more than three seconds to load the web application. Vue.js ensures a smooth experience for the user with a fast bootup time. [Popularity]
It is possible to use Vue.js without installing it by using their CDN in a <script> tag:
https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue/dist/vue.js
However, for larger applications, I recommend using npm to download the framework. To use npm, download Node.js first. After installing npm, execute the following in a terminal:
npm install vue
npm install --global vue-cli
The CLI will be useful for initializing Vue.js projects and running our application server. To get started, type in these commands into the terminal:
vue init webpack myVueProject
cd myVueProject
npm install
npm run dev
vue init webpack creates a webpack module. Webpack will make
use of .vue files and makes it easier
to use both markup with Vue.js syntax.
Vue files also organize the style within a component.
Examples will be given once in the hello vue example below.
cd myVueProject changes the directory to the vue project
that was just created.
npm install checks the dependencies in package.json and installs
any package that is missing.
npm run dev runs the development server and will run the
initial boilerplate Vue.js template.
Go to localhost on port 8080 to see the initial app. The tutorial
will cover some of the
boilerplate code after it covers the basics of Vue.js.
[Installation]
How to use Vue.js¶
For a majority of this tutorial, we will review the basic operations and uses for Vue.js without the complete use of a .vue file. Further into the example app is when the .vue file will be used. For the basics, assume this is a .js file.
Vue begins when a Vue instance is initialized.
var vm = new Vue({
// additional
})
Many developers’ use vm since Vue can be associated with the view model design pattern.
The Vue instance takes in a JSON object as an argument. There are many options that can be passed in. The first and most common option is the data object.
Data can be passed into a Vue instance like this:
var data = {fun: false}
var vm = new Vue({
data: data
})
// vm properties can be accessed like this now
vm.fun == data.fun // when false == false, it returns true
Since the view is reactive, changing a data element will re-render the view model. To access instance properties and methods, use the $ symbol like so:
vm.$data === data // => true
Take advantage of all of Vue’s instance methods using its API reference.
Vue Templates¶
One of Vue’s top highlights is the template syntax. Instead of using JSX like
React.js (which requires prior knowledge of ES6), Vue uses templates that mimic
HTML syntax. Data can be interpolated using the
“double mustache” syntax: {{ }}
//vm.title = "Hello World!";
<h1>Title: {{ title}}</h1>
//javascript can be executed inside the mustaches.
//vm.counter = 0
{{ counter + 1 }}
A powerful way of using templates is taking advantage of Vue directives.
A directive is a special HTML attribute using v- such as v-if.
If data has a list, v-for can be used to iterate through it and easily
repeat HTML elements.
<ul id="example-1">
<li v-for="item in items">
{{ item.message }}
</li>
</ul>
var example1 = new Vue({
el: '#example-1',
data: {
items: [
{ message: 'Foo' },
{ message: 'Bar' }
]
}
})
Using v-model is a powerful way to use Vue’s reactive elements.
It enables two-way binding of data. Try the following for example:
<div id="app-6">
<p>{{ message }}</p>
<input v-model="message">
</div>
var app6 = new Vue({
el: '#app-6',
data: {
message: 'Hello Vue!'
}
})
Changing the input field will change the message since it’s a two-way binding system.
Components¶
Using Vue components is the core of its framework. Components are created into reusable HTML elements. Splitting up the application by components is a common practice for front-end development. Components will encapsulate other components starting at the root level. Think of components being a tree structure starting with the root, usually denoted as the <App/> element, then branching off with other child components. Vue.js provides an implementation of components through the Vue instance. [Tutorial]
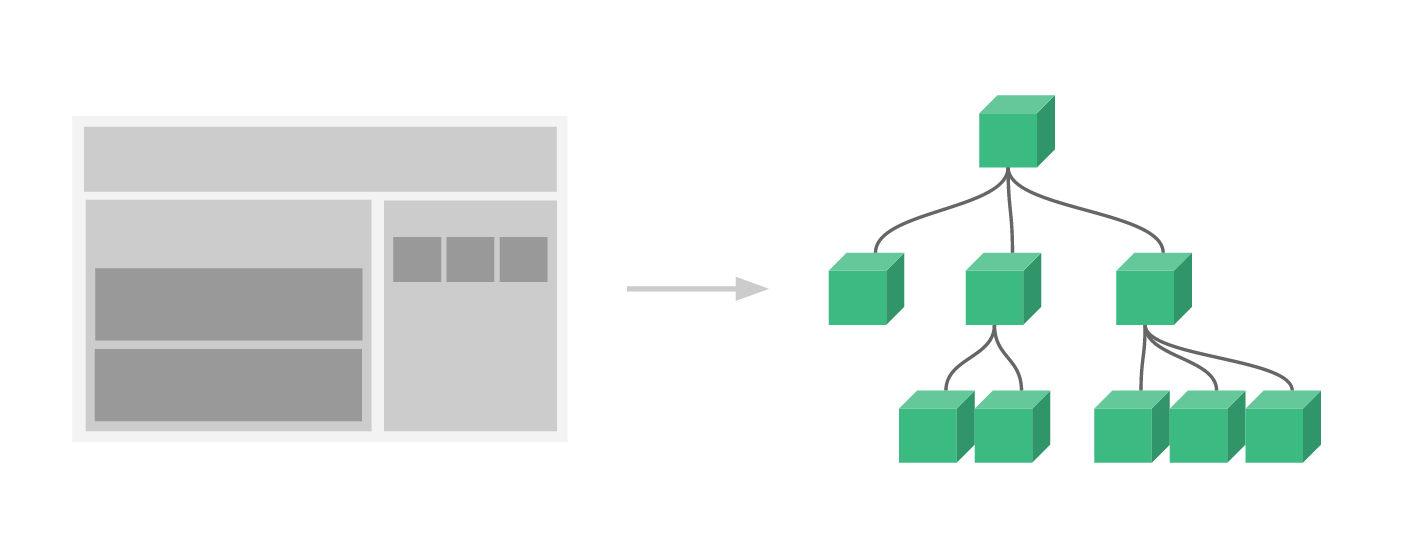
Components usually consist of a template and optional Vue functions. A Vue component can be created like this:
Vue.component('root-app', {
data: function () {
return {
message: "Hello World!"
},
template: <h1> {{ message }}</h1>
}})
//Inside the html
<div id="demo">
<root-app></root-app>
</div>
// In the js
new Vue({el: '#demo});
When initializing Vue instances, use the el option to associate the instance
with the div id inside the html. In the vue components, please note the
template line. With the template defined, vue will
inject <h1> {{ message }}</h1> into <root-app> elements
within the component.
Basic Hello Vue Example¶
In this example, the project structure will be covered and some basic syntax will be explained. This involves more advanced syntax. This example is more tailored for developers who want to build larger applications. To get started, refer to the installation at the beginning of this article. First and foremost, here is a picture of what the directory structure should look like:
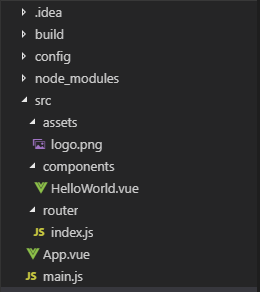
The file that bootstraps the application is main.js:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
Notice the <App/> html element. This is the root of the application.
Add to the components according to the amount you have in the current
template. Since this is just the root level of the application, there is
typically only one component.
Now let’s take a look at .vue files, starting with App.vue:
<template>
<div id="app">
<img src="./assets/logo.png">
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
Typically .vue files have three parts: template, script, and style.
This file represents a component. It has a template and the script attached
to it. Newer to Vue.js is the <router-view/>. This is a special element
that takes a peek at the index.js in the router folder of the project:
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'HelloWorld',
component: HelloWorld
}
]
})
Whatever the current path is, it takes a look at the name and components and loads the appropriate components. The HelloWorld.vue file would be loaded into the root level of the application. [Tutorial]
Conclusion¶
If you are looking to enter the world of front-end development, then Vue.js is a great way to start learning. As seen in several examples listed in this article, anyone who has basic html and javascript knowledge can start Vue.js today. For advanced users, they can also use Vue.js to build lightweight applications. New users can use the CDN to use Vue.js and advanced users can use Vue-CLI and Webpack to build larger applications. The biggest advantage that Vue.js has over other frameworks is the ability to be adopted at any level of an application, from the ground up or it can be incorporated into current applications.
Citations¶
| [WhatIsVue] | “Introduction - Vue.js.” Vue.js, n.d. Web. 11 Apr. 2019. |
| [HistoryOfVue] | Evan You “First Week of Launching Vue”Blog, 11 Feb. 2014, Web. 28. Apr. 2019 |
| [Installation] | “VueJS Environment Setup.”, Tutorials Point, n.d. Web. 4 Apr. 2019. |
| [Popularity] | Nowak, Maja. “Reasons Why Vue.js Is Getting More Traction Every Month.”, Monterail, 19 Dec. 2018, Web. 28 Apr. 2019. |
| [Tutorial] | (1, 2) Eschweiler, Sebastian. “Vue.js 2 Quickstart Tutorial 2017.”, CodingTheSmartWay, Medium, 7 Jan. 2017, Web. 11 Apr. 2019. |